The Max Planck Digital Library has been mandated to discontinue their Elsevier subscription when the current agreement expires on December 31, 2018. Read more about the background in the full press release.
Nevertheless, most journal articles published until that date will remain available, due to the rights stipulated in the MPG contracts to date.
To fulfill the content needs of Max Planck researchers when Elsevier shuts off access to recent content at the beginning of January, the Max Planck libraries and MPDL have coordinated the setup of a common document order service. This will be integrated into the MPG/SFX interface and can be addressed as follows:
Step 1: Search in ScienceDirect, start in any other database or enter the article details into the MPG/SFX citation linker.
Step 2: Click the MPG/SFX button. Note: In ScienceDirect, it appears in the “Get Access” section at the top of those article pages for which the full text is no longer available:
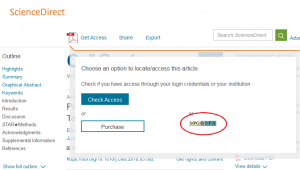
Step 3: Check the options in the service menu presented to you, e.g. free available full text versions (if available).
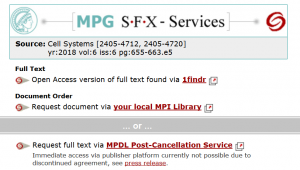
Step 4: To order the article via your local library or the MPDL, select the corresponding link, e.g. "Request document via your local library". Please note that the wording might differ slightly according to your location.
Step 5: Add your personal details to the order form in the next screen and submit your document request.
The team in your local library or at the MPDL will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please feel free to contact us if you face any problem or want to raise a question.
Update, 06.06.2019: Check out our new flyer "How to deal with no subscription DEAL" prepared in cooperation with Max Planck’s PhDnet.